Search
Showing results for "Au"

News & Events
$3.4 million funding boost supercharges fight against RSVNational research led by the Wesfarmers Centre of Vaccines and Infectious Diseases, based at The Kids Research Institute Australia, has secured more than $3.4 million to assess the epidemiology of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) throughout the country and optimise Australia’s immunisation strategy.
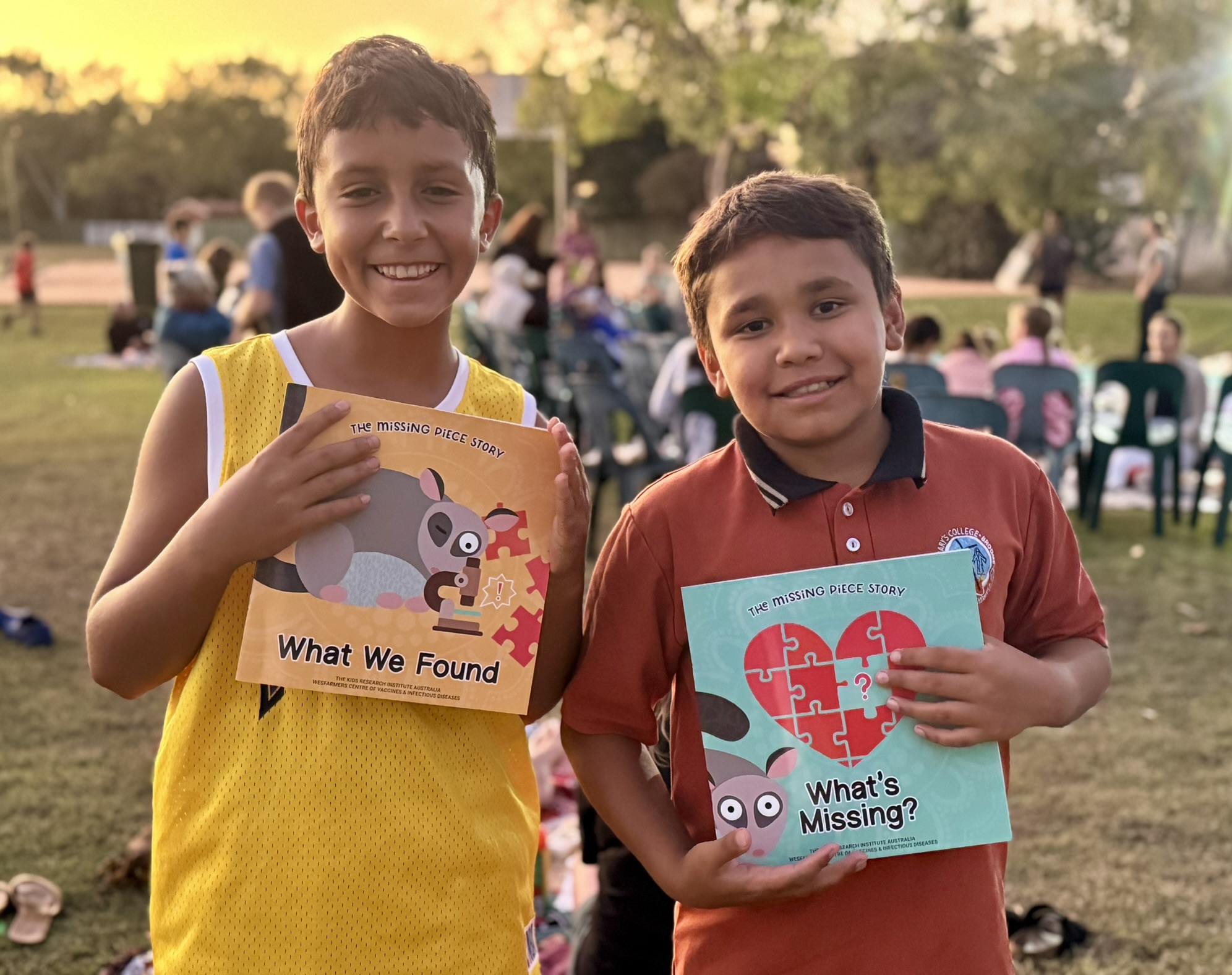
News & Events
Spectacular sunset launch for the Missing Piece Story BooksWesfarmers Centre of Vaccines and Infectious Diseases researchers Dr Janessa Pickering and Dr August Mikucki travelled to Broome last week for the official launch of the long-awaited Missing Piece story books.

News & Events
Rapid diagnosis for childhood brain cancer in WAThe Kids Research Institute Australia's Brain Tumour Research team will develop and implement cutting-edge technologies to revolutionise the speed of brain cancer diagnosis for WA children, thanks to more than $200,000 from Telethon.
CliniKids is putting the ‘evidence’ in evidence-based practice by providing families access to the best scientific-backed therapies as quickly as possible so that all autistic children have the chance to reach their full potential.
Research
Dog Ownership, Physical Activity, and Mental Health in Mid-to-Older Aged Adults: Findings From the HABITAT Cohort StudyDog ownership is a potential strategy for maintaining physical activity levels and supporting healthy aging. This study examined longitudinal effects of dog ownership and dog walking on physical activity and mental health in mid-to-older aged adults.
Research
The role of parenting- and employment-related variables on fathers' involvement in their children's educationParent involvement strongly correlates with children's educational attainment. Sociocultural shifts in parenting roles and shared responsibilities have driven an increase in the need for involvement of fathers in activities to support their children's educational development. Several factors are thought to influence father involvement in children's education; however, the most salient factors remain unclear.
Research
Comparing home polysomnography with transcutaneous CO2 monitoring to laboratory polysomnography in children with neuromuscular disordersClinical utility of home polysomnography in children with neuromuscular disorders is limited by lack of evidence that sleep-disordered breathing can be reliably identified and inability to diagnose hypoventilation because carbon dioxide is not measured.
Research
Validity of using a semi-automated screening tool in a systematic review assessing non-specific effects of respiratory vaccinesThe abstract screening process of systematic reviews can take thousands of hours by two researchers. We aim to determine the reliability and validity of Research Screener, a semi-automated abstract screening tool within a systematic review on non-specific and broader effects of respiratory vaccines on acute lower respiratory infection hospitalisations and antimicrobial prescribing patterns in young children.

News & Events
Active books for active kids!Walk through the jungle, hunt for the bear, or do the animal bop this Book Week! Acting out stories is a wonderful way to encourage active play with your child.

News & Events
New national role for The Kids’ Executive DirectorThe Australian Government has appointed the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Council for 2024 to 2027.
